Chile has faced difficulties with the implementation of a number of reforms recently, which is souring the country’s economic outlook.
Contrary to what has largely been seen in other countries, where reforms tend to imply more liberalisation, Chile is moving to re-regulate its markets and rein in the detrimental liberalisation measures imposed during the 1970s and 1980s.
The two major areas being reformed include the labour market and education policy. The country’s congress passed reforms in April that strengthened the power of unions, and could have a significant impact on the profitability of mining companies – which are already reeling low copper prices.
The country is also looking to implement education reforms, which concern tertiary education, and pension reforms, which are proving to be highly controversial.
However Adam Collins, an economist at Capital Economics said it is too early to gage any real impact from the reform efforts.
“The only real effect that reforms will have on the Chilean economy so far will be on confidence. They are long-term structural reforms, and the fact that they have been opposed is why confidence has been depressed, particularly business confidence.’
Although concerns over Chilean reforms have hit confidence, fiscal and monetary institutions such as the Ministry of Finance and Central Bank have remained notably resilient, and have helped buoy Chile’s economic performance.
Excluding Codelco, Chile’s central government enjoys fairly low levels of leverage at around just under 20% of GDP, which according to Collins is testament to the country’s prudent fiscal policies.
In addition, Chile’s net asset position is also positive. The country also has more net assets abroad than debts.
“On the monetary side, the Central Bank is one of the most credible in the region, and is one of the few that can still cut interest rates even if inflation is above target.”
The Central Bank held interest rates at 3.5% at its last meeting in August. The country’s inflation was reported as rising by 3.4% year-on-year for August, a drop from 4% growth year-on-year reported the previous month.
The Central Bank’s ability to cut interest rates despite inflation means it has more flexibility in responding to rate action in the US.
Furthermore, the Chilean peso is unlikely to be as hard hit by a Fed rate rise as other Latin American currencies, such as the Columbian peso for example. The Chilean peso is currently trading at 669.98 to the dollar.
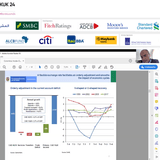
However, despite the potentially negative impact of reforms and the ability of the Central Bank and Ministry of Finance to keep Chile’s economy on track, the price of copper, which constitutes half of the country’s exports, remains the most influential factor determining Chile’s economic outlook. Despite many expecting the economy to pick up to around 3%, GDP growth has been hovering at around 2% over the last year. Q2 2016 GDP growth amounted to 1.5% year-on-year.
Copper is currently trading at US$4,648 per metric tonne according to Bloomberg, down from US$7,600 per metric tonne at the beginning of 2012.
According to Collins, copper prices are expected to rise over the next few years, which will improve Chile’s economic outlook.
“The massive drought from the fall in mining investment is starting to ease, and as Chile does not have any major external imbalances, the economy is likely to pick up, but growth will be weaker than it has been over the last decade.”