In November, the CBRT lifted the one- week repo and overnight lending rates by 50bp and 25bp to 8% and 8.5% respectively, the Bank’s first rate hike in nearly three years, and kept the overnight borrowing rate steady at 7.25%. In January, the CBRT raised the overnight borrowing rate by another 75bp to 9.50%, but kept other key rates on hold – against market expectations.
“The slowdown in aggregate demand contributes to the fall in inflation. However, exchange rate movements due to recently heightened global uncertainty and volatility pose upside risks on the inflation outlook,” the CBRT said in a statement on its website.“The committee decided to implement monetary tightening to contain the adverse impact of these developments on expectations and the pricing behaviour,” it said.
The lira saw a brief spike following the move in November, jumping from 3.419 per US dollar to 3.381, but the rally appears to have been short lived, having dropped to almost 3.85 against the US dollar at the time of writing. Analysts at JP Morgan don’t think it will end there; the investment bank is forecasting the lira could stabilise at around 3.65 to the US dollar by the end of 2017, and slide even further if the CBRT doesn’t continue tightening.
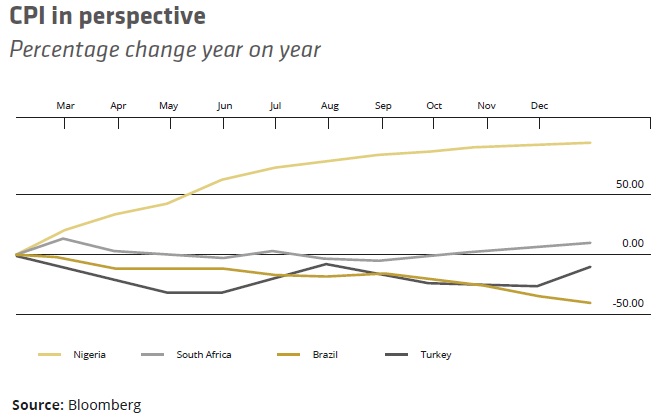
The lira has been one of the worst performers among EM currencies in 2016, and has lost nearly 18% against the US dollar since mid-September, and almost 10% to the euro in 2017.
The yield on benchmark 10-year bonds sat at 11.30% in spot trading at the time of publishing, and dropped slightly to 11.21% in Friday-dated trades.
The interest rate hike came less than a day after President Recep Tayyip Erdogan criticised the country’s bankers and monetary policymakers, urging them to lower interest rates during a speech delivered at the meeting of Standing Committee for Economic and Commercial Cooperation of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation in Istanbul.
He went so far as to suggest a failure to comply with his wishes could result in “intervention”, but stopped short of specifying what that would entail.
Investors have grown increasingly concerned with Erdogan’s willingness to intervene in monetary policy, which could put added pressure on the struggling economy.
“Investors were largely willing to put up with a one-man regime so long as the policy environment remains predictable and the boundaries between institutions respected – and you couldn’t ignore the growth rates we were seeing there, or the strength of some of the country’s biggest firms,” said one London-based EM investor.
“That’s starting to change. Growth has been sagging for some time now. And Erdogan, with a shocking degree of openness, has suggested he is willing to directly intervene in both fiscal and monetary policy. That worries us.”
The country’s GDP grew 0.3% in Q3 2016, down from a relatively modest forecast of 1%. It is forecast to put in 0.3% growth in Q4.
Erdogan has a worrying history of intervention. In March 2014, the Turkish President criticised then Central Bank Governor Erdem Basci over the Bank’s inability to tackle inflation, pressuring Basci to raise rates.
More recently, the President requested all of the country’s mortgage lenders reduce the interest rates on loans in order to ease lending conditions, and said those that didn’t comply were committing an act tantamount to “treason”. All of the country’s mortgage lenders have since complied with the request.
Some analysts doubt the effectiveness of the most recent rate hike. With the US looking to raise interest rates about three times in 2017, the CBRT’s most recent move will be netted out for the most part – which, coupled with the Bank’s struggle to keep inflation within target range, will likely mean more hikes this year.
“I don’t think the rate hike will be enough to stabilise the currency, which, in my view, is the best outlet to express bearish views on Turkey,” said Inan Demir, an EEMEA economist at Nomura, adding that the impact on credit will likely be muted as well.
“There will probably be criticism from Erdogan about the interest rate hike, but the reality is the most recent hike is unlikely to have a meaningful impact on the domestic credit conditions. I would say continuation of the lira’s depreciation is more damaging for domestic demand compared to rate hikes,” Demir said.
With the economy on a weak footing, exacerbated by a credit rating downgrade in September and a currency in free-fall, it is clear to most that the CBRT was left with few options but to increase interest rates. In the run-up to the move, top members of the country’s economic team – including Deputy Prime Minister Nurettin Canikli – have brushed off suggestions that the currency is suffering, worrying investors.
With Erdogan vehemently supportive of further easing measures and the CBRT moving in the opposite direction, questions remain over whether the dynamic could provoke a standoff. Other government officials, meanwhile, have looked to focus attention awat from the country’s currency woes. Bulent Gedikli, an adviser to the Turkish President, took to Twitter to protest the broad obsession with the country’s currency, saying that there needs to be greater focus on the structural reforms, and that “only so much can be done by limiting the lira.”
“I hope it doesn’t come to that. But let’s be honest, moving in the opposite direction of Erdogan seems to come at a cost these days,” the investor said.